The quality of our water is a direct link to the quality of our health.
Understanding the full scope of benefits and risks associated with utilizing water from a rainwater catchment system is crucial. In Hawai‘i, there are no regulatory bodies monitoring the safety of individual catchment systems. Therefore, it falls upon the owner or user of the system to be knowledgeable about maintaining the water source and utilizing it in a manner that is safe and suitable for themselves, their family and guests.
An effectively designed rainwater harvesting system should be user-friendly and necessitate regular maintenance. Consistent upkeep of such a system is essential to uphold its optimal performance. Neglecting maintenance can result in compromised water quality, reduced water availability, potential pathogen contamination, and ultimately, adverse effects on both the rainwater harvesting system and the health of the end user. The maintenance plan should encompass all components from the collection surface (roof) to the point of use (faucet).
Contaminants posing a risk to water quality can be categorized as biological, chemical, or metallic in nature. Each type of contamination underscores the importance of treating stored rainwater for disinfection or purification. Biological threats encompass pathogens that can lead to various diseases. Examples include leptospirosis, giardiasis, and cryptosporidiosis, which are caused by organisms present in the gastrointestinal or urinary tracts of mammals. Additionally, birds, reptiles, slugs, and geckos may also carry pathogens responsible for diseases such as campylobacteriosis, salmonellosis, and rat lungworm disease.
Heavy metals represent the third significant source of potential contamination, often originating from building materials that release elements like lead, zinc, or copper into the water. Galvanized steel, for instance, has the potential to leach cadmium. Additionally, heavy metals can be introduced through volcanic emissions and pesticide drift. In Hawai‘i, the majority of heavy metal issues are linked to lead leaching from paint, nails, flashings, and other construction materials. Rainwater, typically acidic, can expedite the leaching process of metals and various other chemicals from building materials.
Acid rain, with a pH below 5.6, is typically linked to human activities, particularly the combustion of fossil fuels which releases excessive nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere. However, it can occur globally. In Hawai‘i, volcanic emissions are the primary cause, notably sulfur dioxide (SO2) released during eruptions. This SO2 reacts with water vapor in the atmosphere, forming dilute sulfuric acid that falls as acid rain. According to the College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources, Kilauea volcano emits 350 metric tons of SO2 per day during eruptive pauses and 1850 metric tons per day during active eruptions.
The impact of acid rain on copper piping is more pronounced when the pipes transport hot water, increasing the leaching reaction. Even before copper levels become problematic, leached copper can leave a blue-green stain on porcelain and fiberglass sinks and tubs. Iron typically leaves a brown stain, while lead is less likely to cause discoloration. The University of Hawai'i provides subsidized water testing services. For further details, visit www.tiloscleanwater.com/clean-water-partners.html
Acid rain collected in catchment systems lacks the chance to interact with the earth's natural buffers. In Hawai‘i, catchment tanks situated downwind of volcanic plumes, especially in regions like Kā‘ū and South Kona, frequently record pH levels as low as 4.
Poly Tanks Galvanized Steel tanks Whole House Disinfection
Suggested Maintenance Schedule

Please be aware: the information provided below doesn't cover all maintenance aspects for your rainwater harvesting system.
What it offers are sensible suggestions and recommendations to seriously consider. Your health relies on having access to clean, pathogen-free water. As a Rainwater Harvester, your relationship with water is crucial for your well-being and vitality.
Water sustains all life forms. Water equals Life. Clean Water equals health.
Rainwater Harvesting promotes self-reliance, especially in a region situated in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, atop five volcanoes, surrounded by the Ring of Fire, where every moment counts, and living with purpose is essential!
What it offers are sensible suggestions and recommendations to seriously consider. Your health relies on having access to clean, pathogen-free water. As a Rainwater Harvester, your relationship with water is crucial for your well-being and vitality.
Water sustains all life forms. Water equals Life. Clean Water equals health.
Rainwater Harvesting promotes self-reliance, especially in a region situated in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, atop five volcanoes, surrounded by the Ring of Fire, where every moment counts, and living with purpose is essential!
1. Assess the roof's condition. Examine for any accumulation of debris from overhanging vegetation and signs of deterioration or rust on roofing materials. If any issues are detected, address them promptly by fixing or removing them. Perform this inspection on a monthly basis and after periods of windy weather.
2. Inspect and clean gutters and downspouts on a monthly basis to remove any debris. Accumulated debris can negatively impact water flow and result in diminished water quality. It's advisable to conduct thorough cleanings a few times a year, particularly after windy storms.
3. Clean and inspect the pre-tank filter and First Flush Diverter on a monthly basis. These components ensure that cleaner water enters the tank, thus extending the tank's cleanliness over time.
4. Perform a monthly inspection of the storage tank. Examine all inlets and outlets to ensure there are no gaps, and that any openings are screened. Inspect the area around the tank for signs of excess water, which may indicate a leak. Replace the nylon mesh on overflow and intake pipes. Look for signs of erosion around the tank. Check the tank lid to ensure that surface debris and runoff cannot enter the tank. Promptly address any issues identified during this inspection.
5. Inspect the water distribution piping and pump. Examine the distribution piping for any signs of leaks.
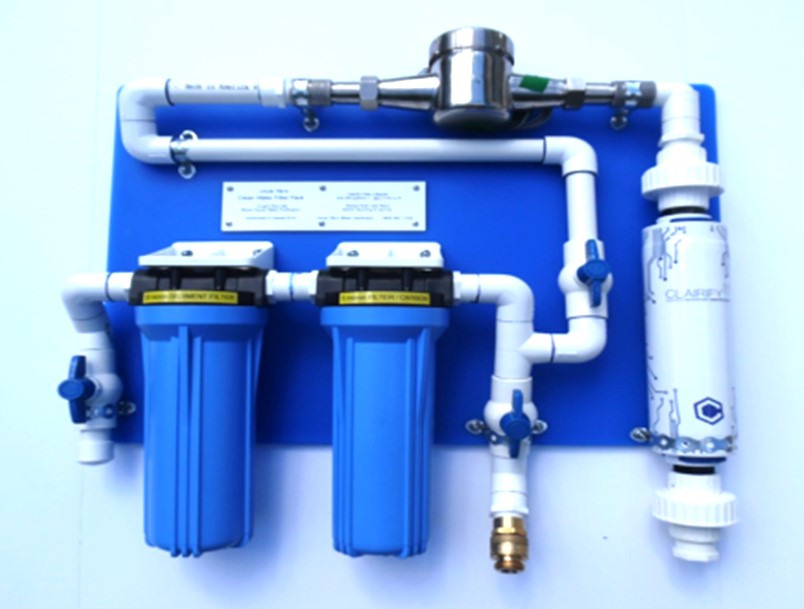
6. Review the final water treatment system and replace any necessary parts. Keep a small notebook nearby to record filter change dates. If the rainwater harvesting system is utilized indoors, consider additional water treatment after the storage tank. This could involve sediment filters, carbon filters, Quantum Disinfection, Class A ultraviolet lights, and more. Check this equipment monthly, and replace consumable parts like filter cartridges and Class A ultraviolet light bulbs or quartz sleeves according to the manufacturer's instructions. Moreover, if the water is intended for potable use (drinking, cooking, bathing, handwashing, etc.), it's essential to test the water quality annually.
Follow the chlorine treatment guidelines provided by Patricia Macomber of the College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources, aiming for a recommended level of 1 ppm. Ensure you have chlorine test kits available. Most household bleach products contain sodium hypochlorite as their active ingredient. Check the label to determine the sodium hypochlorite content. Avoid using scented bleach or products with additional additives. Some household bleach products may contain 6 percent sodium hypochlorite. In such cases, use 2 ounces (1⁄4 cup) per 1000 gallons during rainy periods and 4 ounces per 1000 gallons during dry periods.
Chlorine Tablets - * DO NOT USE POOL TABS WITH STABILIZER - THE STABILIZER IS CYANURIC ACID.
There are tablets made for portable water. Always look for the NSF rating!
There are tablets made for portable water. Always look for the NSF rating!
Minerals can be introduced to elevate pH levels in your tank by incorporating substances like baking soda (sodium bicarbonate), granulated calcium carbonate (calcite), or sodium carbonate (soda ash). Baking soda is commonly preferred due to its accessibility and affordability. Additionally, it functions as a neutralizer, ensuring pH adjustment without concerns of excessive elevation. According to Patricia Macomber from the College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources, determining the appropriate dosage can be challenging due to the diverse factors involved in each system.
To incorporate chlorine and/or baking soda into your tank, dissolve them in water first and then pour the solution into the tank. Stir the mixture thoroughly to ensure even distribution.
Water with a pH of 7.0 is considered neutral. An ideal pH range falls between 6.5 and 8.5. Maintaining a pH above 6.0 is advisable to minimize leaching, especially in systems containing metal components. When consuming acidic water, it's important to be cautious about its potential impact on dental health.
Water Testing for Private Water Supplies
If your drinking water doesn't originate from a public water system, such as from a household well or rainwater, it's solely your responsibility to ensure its safety. Therefore, it's highly advisable to conduct routine testing for several common contaminants. Even if your water currently meets safety standards, regular testing is valuable as it establishes a history of water quality, which can be instrumental in addressing any future issues.
For more information on local Hawai'i water testing:
www.tiloscleanwater.com/clean-water-partners.html
www.tiloscleanwater.com/clean-water-partners.html
For additional information and learning opportunities join Uncle Tilo in his offering