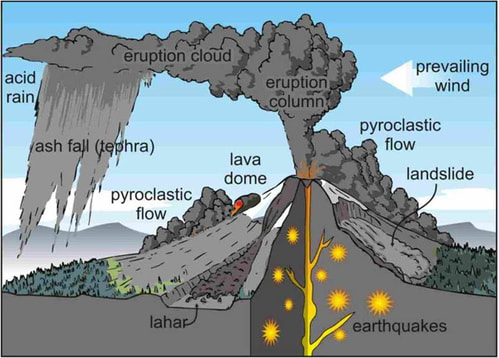
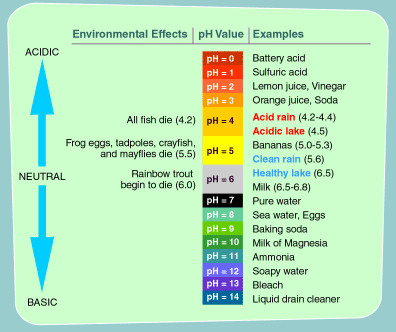
Did you know......seriesACID RAIN AND PREVAILING WINDAcid rain is a broad term that is often used to describe several forms of acid deposition. Wet deposition is when rain, snow, fog, or mist contains high amounts of sulfuric and nitric acid. When sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are emitted into the atmosphere, they dissolve in water and fall as precipitation. Dry deposition occurs when dust and smoke that contain high amounts of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides settle to the ground, or onto buildings, cars and vegetation. These gases are converted to acids when they contact water. The acidity of acid rain can vary. Pure water has a pH of 7 and normal rainwater has a pH around 5.6. In 2000, the most acidic rain that fell in the United States had a pH of 4.3. WHERE DOES ACID RAIN COME FROM?Acid rain develops when sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides enter the atmosphere. While natural processes, such as the eruption of a volcano or decomposing vegetation, can emit sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the air, acid rain is primarily caused by excessive emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides as a result of human actions. The primary cause of nitrogen oxide emissions are vehicles, which account for about 60 percent of all nitrogen oxide emissions. However, emissions also come from furnaces, boilers and engines. CAN ACID RAIN MAKE DRINKING WATER UNSAFE?Water that is slightly acidic should not be dangerous, as there are many food that have low pH value; for example, lemon juice, soda pop and oranges has a pH range of 2.4 and 3.6. However, a low pH can indicate that there may be other contaminants in the water, because if pollutants have been added to a water source, the pH typically will change. Water treatment facilities monitor the pH level of the water while they are treating it for municipal use and therefore Rainwater Harvesters should also. Acidic or basic water is harder to disinfect than water with a pH that is closer t 7.0.
|